3D printer extruder directly impacts the final quality of your prints. A high-quality extruder can control filament extrusion accuracy and flow, leading to faster 3D printing speed with fewer defects like clogging and delamination. Conversely, a poorly chosen extruder can result in frustrating prints and wasted filament. Therefore, choosing the best extruder is essential for smooth and successful 3D printing.
If you’re unsure how to pick one, this article will guide you. We will provide an in-depth discussion of everything you need to know about 3D printer extruders to help you pick the best option. Let’s begin!
| Note: ZWSOFT has recently launched ZW3D 2025, the best solution for CAD/CAE/CAM. Compared to the previous version, ZW3D 2025 offers an improved user experience and more advanced features to expedite the modeling process. If you’re interested, download it and give it a try. |
What Is a 3D Printer Extruder?
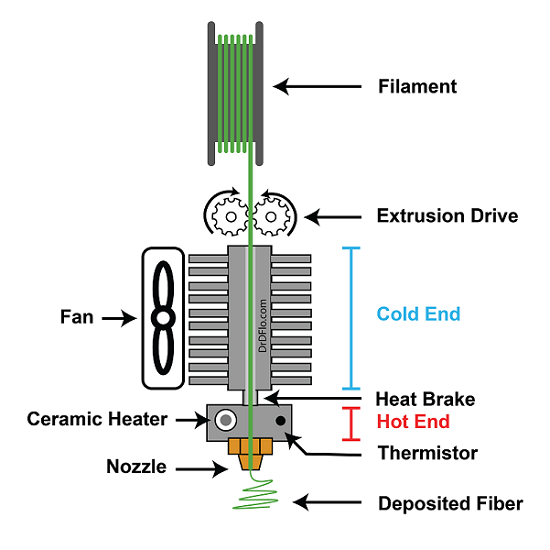
An extruder is an essential part of your 3D printer, which is responsible for melting and precisely ejecting filament through a nozzle to create objects layer by layer along a specific path. This is achieved through a multi-step process that works with the cold end and the hot end of the 3D printer extruder, involving feeding, heating, and flow control.
The cold end pushes the filament towards the hot end, which then heats the filament to its melting point and precisely controls its extrusion. This is why extruder performance is so important, as it directly affects the accuracy, surface smoothness, and 3D printing speed of your prints.
What Is the Structure of a 3D Printer Extruder?
As we mentioned previously, a 3D printer filament extruder relies on the collaboration of two key parts: the cold end and the hot end. Only when they work together can the 3D printer extruder precisely and consistently control the filament extrusion, thereby enabling high-quality and complex 3D model printing.
Cold End
Typically located at the upper part of the extruder, the cold end includes an extruder motor, gear, tensioner, and filament Sensor. This setup helps to keep the filament cool and prevents it from softening or melting too early before it reaches the hot end. This is important for ensuring a steady and precise material feed, facilitating consistent 3D printing quality.
- Extruder Motor: This is the core part of the cold end that drives filaments into the extruder. Its performance directly affects the filament’s feeding speed and accuracy. Poor extruder motor performance can lead to uneven feeding, leading to poor print quality.
- Gear: The gear, which works with the extruder motor, controls the feeding speed and direction of filaments. In general, a gear with fewer teeth or a smaller diameter will rotate faster, leading to a higher filament feed rate.
- Tensioner: This is used to control the pressure on the gears to ensure the filament feeds smoothly. If the pressure is too low, the printing filament may slip and cause low printing quality; if it is too high, it may make the filament get stuck and even damage your printer.
- Filament Sensor: A filament sensor is used to monitor the filament’s feeding status. When the filament runs out or breaks, the sensor sends a signal to the controller to pause printing and notify you to change the filament. This helps prevent printing failures or quality issues caused by filament problems.
Hot End
Meanwhile, the hot end, situated closer to the nozzle, melts the filament and controls the filament extrusion process, ensuring a smooth and consistent flow. When selecting a 3D printer extruder, choosing a well-built hot end is essential to getting optimal 3D print quality. This section typically consists of several components, including:
- Heat Sink: Located on the upper part of the hot end, it is essential for temperature control. A good heat sink can prevent excessive heat around the hot end, reducing potential issues such as drawing, clogging, and filament decomposition.
- Cooling Fan: A cooling fan is placed near the heat sink to enhance heat dissipation. This can effectively maintain a stable working temperature at the hot end.
- Heat Break: It is usually made of high-temperature resistant materials such as titanium alloy. This prevents the filament from melting prematurely before entering the nozzle and minimizes heat transfer to other components.
- Heater Block: It is for heating the filament to a molten state for extrusion. A good heater block can respond quickly to temperature changes and maintain a stable operating temperature for the 3D printer extruder.
- Heater Cartridge: A heater cartridge consists of a high-temperature resistance wire or heating resistance tube that heats the metal shell of the heater block through an electric current. This ensures that the filament reaches melting temperature quickly.
- Thermistor: This is used to measure and monitor the temperature inside the heater block to avoid overheating or underheating of the filament, guaranteeing printing quality and stability.
- Nozzle: It is the final component of the hot end for extruding the melted filament. Its diameter determines the thickness of the filament line and therefore the print accuracy.
Types of 3D Printer Extruders
Learning about the types of 3D printer extruders is crucial for obtaining precise and efficient prints. There are currently various commonly used extruders in 3D printers to choose from, depending on the drive mechanism and filament delivery method:
Single Extruder
A single extruder, also known as a direct extruder in 3D printers, places the extruder motor on top of the hot end, connecting it right to the nozzle. This setup delivers a shorter filament delivery path, allowing for more precise filament flow control, and better control of filament movement, pressure, and retraction.
Therefore, it is ideal for printing delicate or flexible filaments that can be easily damaged. However, since the motor is installed on the print head, the overall weight can be increased, potentially limiting the 3D printer’s maximum printing speed and acceleration.
Dual Extruders
The biggest feature of the dual extruder in 3D printers is that it can install two extruders at the same time, allowing the 3D printer to use two different filaments or colors simultaneously during the printing process without having to manually change the filament. This feature is particularly useful when you need to print support structures, multi-material, or multi-color designs, such as complex prototyping and artistic creations.
However, compared to single extruders, these multi extruders for 3D printers typically require more maintenance and are more expensive.
Bowden Extruder
Unlike the previous two 3D printer extruders, a Bowden extruder is usually mounted on the frame of the 3D printer, away from the hot end. As a result, filaments are fed through a long PTFE tube (often called a Bowden tube), instead of having its cold end located directly right next to the hot end like others.
This helps reduce the print head’s overall weight, resulting in faster 3D print speeds. However, a long filament path is also more likely to lead to clogging issues.
How to Choose a 3D Printer Extruder?
After reading the above, you may deeply understand what a 3D printer extruder is and its crucial role in the printing process. However, it is not easy to choose the best 3D printer extruder. In addition to reading user reviews, there are several factors to consider:
- Define Your Printing Needs: To begin with, clarify your printing needs, which will determine the filament, print size, and print accuracy you need.
- Pick the right Extruder type: Common types include single extruders, dual extruders, and Bowden extruders. If you need to use two different filaments or colors at once, then a dual extruder can be the best for your 3D printer.
- Choose Print Filaments: Make sure the extruder is compatible with the filament you plan to use. For example, if you need to 3D print rafts that require greater adhesion and stability, consider a 3D printer extruder that can adjust the distance between the extruder and the print bed for optimal raft adhesion.
- Consider 3D Printing Speed and Accuracy: These are the most crucial factors when choosing the best 3D printer extruder. In general, single extruders usually provide better printing accuracy, while Bowden extruders can provide faster printing speeds.
- Ensure Compatibility: Since some extruders may require specific software support or additional hardware installation, make sure the extruder you choose is compatible with your 3D printer.
- Mind Your Budget: 3D printer extruders vary greatly in price, ranging from tens of dollars to thousands of dollars. Be sure to consider your budget before making a decision.
FAQs About 3D Printer Extruder
What Should I Do If My Extruder Is Clogged?
There are two practical ways to unclog your extruder:
- If it is only slightly clogged, you can try to clean it out with a probe or a thin wire such as a guitar string. However, this method can scratch the nozzle’s interior.
- For more serious clogs, disassembling the printhead for cleaning is recommended.
Clogged extruders can cause various issues, including uneven filament extrusion, very thin extruded filament, the 3D printer stopping extruding mid-print, or even the 3D printer not extruding at all. These problems are often due to a small amount of filament residue buildup on the hot end or nozzle. If the problem persists after trying these methods, contact your printer manufacturer for assistance.
What to Do If the Extruder Is Leaking or Dripping Material?
Leaking or dripping material from the 3D printer extruder can result in a rough and defective surface on your prints, ultimately affecting the final quality. When you encounter these problems, it is recommended to first check the hot end, nozzle, and other parts to make sure they have been properly tightened and installed. Otherwise, filaments will not flow out properly with loose components, resulting in leakage or dripping.
It is also a good idea to adjust your print settings. For example, lowering the extruder temperature accordingly, as excessive heat can cause premature melting and dripping. You can also try increasing the 3D printing speed, which reduces the time the material stays in the nozzle, reducing the likelihood of leaks or drips.
If your 3D printer uses a Bourdon Extruder, leakage or dripping is likely caused by aged or worn PTFE tubing. Please make sure that the PTFE tubing is securely connected to other parts to prevent material leakage.
By following these methods, you can effectively solve the 3D printer extruder leakage or dripping problem. If you still cannot solve the problem, it’s best to contact a professional for further help.
Conclusion
The 3D printer extruder is an important part of a 3D printer that directly affects print quality. To help you better understand extruders, this article delves into the basics, exploring their common types, and how to choose and buy them.
Moreover, detailed and effective solutions to troubleshoot their common problems are also available here, helping your prints run smoothly. By reading this article, you are now equipped to pick the best 3d printer extruder easily for your needs out of the many options available. If you find this article useful, please consider sharing it to help others.
.png)