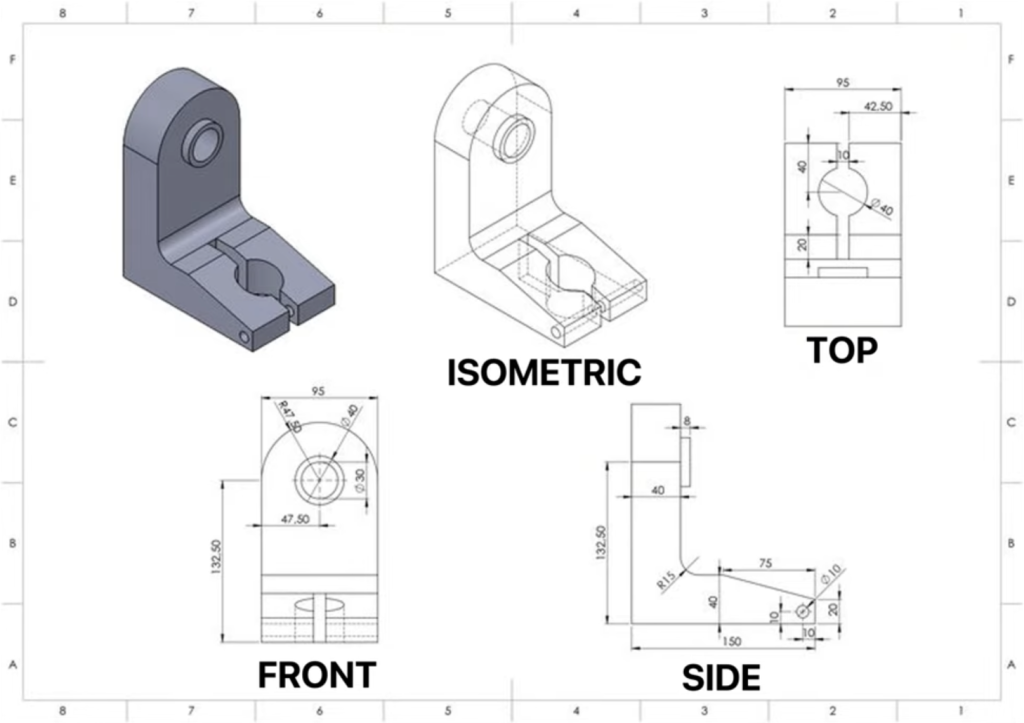
Choosing the right CAD software is essential in mechanical engineering. Whether you’re sketching a piping layout, designing an HVAC system, or assembling detailed parts, your choice between 2D and 3D CAD affects your workflow, accuracy, and costs.
But how do you decide? When is 2D CAD the better choice? When should you go for 3D CAD? In this guide, we’ll explain the strengths of each and how to combine them. Let’s get started.
Hear What a Professional Engineer Has to Say First
Before diving deeper, watch the following video. A professional engineer explains the key differences between 2D and 3D CAD. You’ll also learn practical tips and real-world examples. Whether you’re new to CAD or a pro, this video will help you make better decisions.
Why 2D CAD Is Still Indispensable
Despite being one of the oldest forms of computer-aided design, 2D CAD continues to be an irreplaceable tool for many engineers and industries. Why? Because sometimes, simplicity is exactly what you need.
Advantages of 2D CAD:
- Speed: Creating 2D drawings is fast, especially for simple designs.
- Ease of Use: It’s straightforward and requires less training.
- Light on Resources: Runs on most computers without heavy system demands.
- Clear Communication: Easy to share with contractors and manufacturers.
Who Uses 2D CAD?
- HVAC Designers: For ductwork and ventilation layouts.
- Piping Engineers: For hydraulic circuits and pipeline schematics.
- Manufacturing Teams: For CNC patterns and technical drawings.
- Electrical Engineers: For wiring and control panel diagrams.
Even as 3D CAD becomes popular, 2D CAD remains a go-to tool for many professionals because of its speed and simplicity.
How 3D CAD Takes Design to the Next Level
Sometimes, 2D CAD isn’t enough. That’s where 3D CAD comes in. It allows you to visualize and test designs before they are built.
What Makes 3D CAD Unique:
- Realistic Views: Rotate and zoom to see designs from every angle.
- Simulations: Test your design for stress, heat, and movement.
- Prototyping: Create files for 3D printing easily.
- Collaboration: Use 3D models to explain your design to others.
Industries leveraging 3D CAD include:
- Automotive Engineers: For designing engines and transmissions.
- Aerospace Designers: For modeling turbine blades.
- Product Designers: For creating detailed prototypes.
With 3D CAD, you’re not just designing—you’re solving problems before production.
The Perfect Workflow: Blending 2D and 3D CAD
For many projects, the best solution isn’t choosing one over the other—it’s using both. Combining 2D and 3D CAD allows engineers to play to the strengths of each tool at different stages of the design process.
Here’s an example of a typical workflow:
- Concept Phase: Use 2D CAD to sketch out rough ideas and basic layouts.
- Detailed Design Phase: Transition to 3D CAD to create accurate models and run simulations.
- Documentation Phase: Generate 2D drawings from the 3D model for manufacturing and assembly instructions.
This hybrid approach ensures that you work efficiently without sacrificing accuracy or detail. For an example of combining these methods in architectural projects, explore remodeling design.
Why ZWCAD Is a Trusted Tool for Engineers
If you’re looking for a CAD tool that can handle both 2D and 3D workflows seamlessly, ZWCAD is worth considering. Trusted by global brands like Bosch and Panasonic, ZWCAD strikes the perfect balance between power, performance, and affordability.
What Makes ZWCAD Stand Out:
- Speed and Efficiency: ZWCAD is faster than many competitors, handling large files and complex designs with ease.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Supporting file formats like DWG, DXF, and STEP, ZWCAD ensures smooth collaboration with other tools and teams.
- Smart Features: From paper-to-digital vectorization to advanced 3D modeling tools like the 3D Gizmo and ViewCube, ZWCAD offers features that enhance productivity.
- Perpetual Licensing: Unlike subscription-based models, ZWCAD offers a one-time purchase option, making it a cost-effective choice for businesses and individuals.
It’s this combination of performance and value that has made ZWCAD a favorite among engineers worldwide.
Note:
ZWSOFT has released ZWCAD Flex, a subscription-based CAD solution currently available exclusively in the United States and Canada.
Users outside these regions are encouraged to contact their local ZWSOFT sales team to explore perpetual license options for ZWCAD.
Real-Life Examples: When to Choose 2D vs. 3D
Still unsure about when to use each type of CAD? Let’s look at some practical examples:
- Designing a Piping System: Start with 2D CAD for schematics to map out the layout, then move to 3D CAD to check for fit issues and simulate fluid flow.
- Creating a Gearbox: Use 3D CAD to model each component and simulate its operation, then generate 2D drawings for manufacturing.
- Developing an HVAC System: Begin with 2D CAD to draft duct layouts, then use 3D CAD to model the system and ensure everything fits within the space.
Start Mastering CAD for Smarter Designs Today
Whether you’re drafting a quick piping schematic or building a complex assembly, CAD tools are at the heart of modern engineering. Mastering both 2D and 3D CAD isn’t just about learning software—it’s about using the right tools at the right time to create smarter, more innovative designs.
With tools like ZWCAD, you can seamlessly integrate 2D and 3D workflows, optimize your projects, and bring your ideas to life. Ready to see for yourself? Try ZWCAD for free and discover a faster, smarter way to design.
.png)