CAD technology is widely used in various fields, such as machinery, construction, electronics, and other industries. Whether you are a technician or a front-line worker, learning CAD can not only teach you how to draw but also help you improve your professional expertise.
However, many people tend to overlook the importance of selecting the appropriate CAD file format. It is crucial to choose the correct file format because CAD files generated between different versions of CAD software may be incompatible. Furthermore, each CAD file format is suitable for different file types. Selecting the right file format can enhance work efficiency and better showcase your design projects. If you are not familiar with CAD file formats yet, please continue reading this article. In the following sections, we will introduce you to what a CAD file is, what the most common CAD file formats are, and more.
More Readings:
- How to Convert DWG to DXF in 2024 (6 Methods)
- 8 Best 2D & 3D CAD Software for Beginners in 2025
- How to Convert DXF to PDF for Free (A Complete Guide)
What Is a CAD File? What Are CAD File Types?
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) file is generated by CAD software programs, including information such as geometric data, manufacturing data, material properties, and other product/process data. It is a digital file that contains 2D or 3D designs of physical objects and can be used to create models or design plans by designers, engineers, manufacturers, scientists, and digital artists.
Generally speaking, there are two main CAD file types: native formats and neutral formats.
- Native formats are formats that are proprietary to a specific CAD software and are the copyrighted intellectual property of the system used. Moreover, this format can create and give you access to as much information as possible about your 3D CAD files. If using corresponding CAD software, it will offer more information and be more accurate than neutral CAD format files.
- Neutral formats are open formats and not protected by any specific CAD program copyright. The neutral CAD file formats are interoperable between different CAD software, allowing different applications to import and export data. While there is a certain loss of detail when using them, they are great for collaborative work.
Here are a few file extensions of native and neutral 2D or 3D CAD file formats that will let you save your work properly:
| CAD File Extensions | |
| Native CAD formats | .dwg, .CATPart, .CATProduct, .ptc, .prt, .asm, .ipt,.aim, .sldprt, .sldasm |
| Neutral CAD formats | .igs, .iges, .stp, .step, .stl, .qif, .pdf |
CAD File Capabilities: Storing Properties
You may be curious, what exactly can be stored in a CAD file? In fact, all data from design to production can be stored in a CAD file, including Geometry Representation, Topology, Product Design, Meta-Data, and Visual Representation of Qualities.
- Geometry Representation. It defines the shape of the element. Geometry objects store detailed information about part dimensions and geometric properties, such as surface area, volume, and centroid. Also, it is one of two components of the B-Rep model, which is the most common way of describing CAD models. Additionally, another component is topology.
- Topology. In a CAD file, topology outlines how surfaces and edges are connected, continuous, and bounded. Topological shapes include entities such as solids, sheets, wireframes, and acorns, as well as elements such as shells, faces, edges, and so on.
- Product Design. This usually refers to the hierarchical structure of individual objects and interconnected object groups. In addition, product structure data provides a directory hierarchy on the left side of the screen in most CAD software packages.
- Meta-Data. It consists of object names and IDs, layers, product and manufacturing information (PMI), and validated attributes. When a 3D CAD model has built-in metadata, each download will include object names and IDs, layers, custom properties, manufacturer information, and more. Without metadata, all information related to the part will be lost once it enters the design.
- Visual Representation of Qualities. A CAD file contains visual properties such as color, light, texture, materials, etc., which play a crucial role in presenting the model to stakeholders. All these features work together to make the CAD model stand out and vividly enhance its structure and functionality.
Now, you have a general understanding of CAD files. Next, we will show you the 15 most commonly used CAD file types and extensions, so that you can have a deeper understanding of CAD.
15 Commonly Used CAD File Types and Extensions
In addition to the familiar .dwg files, there are also various CAD file extensions, such as .dxf, .stl, .iges, .step, .pdf, etc. Learning about the extensions and functions of some commonly used CAD files is very helpful for you to gain a deeper understanding of CAD. Therefore, here is a brief introduction to 15 commonly used CAD files.
DWG
- File extension: .dwg
- Type: Native
DWG, a native file format of AutoCAD software, which is a 2D and 3D computer-aided design (CAD) file format, is widely used in the architecture and engineering fields. DWG files can contain information such as graphics, layers, lines, colors, text, and metadata, and can be read and edited by most CAD software. When it comes to file versions, different versions of software can affect DWG interoperability. DWG files can contain rich metadata but may not capture component or assembly information. When sharing DWG files, it is key to confirm that the recipient is using the appropriate software version.
DXF:
- File extension: .dxf
- Type: Neutral
DXF is a CAD data file format developed by Autodesk for exchanging CAD data between AutoCAD and other software, containing layer information, geometric data, and coordinate systems. It is an open vector data format, including ASCII and binary formats. The former has good readability but large space, while the latter has small space and fast reading speed.
STL:
- File extension: .stl
- Type: Neutral
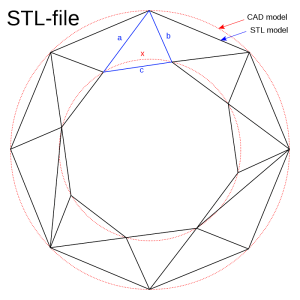
STL (Stereolithography) is a file format originally used for 3D printing purposes. Today, it is widely used in 3D printing, laser scanning, rapid prototyping, and CAM workflows. But most general-purpose CAD software packages also support STL. The STL file only defines the surface geometry, whose structure is represented by a list of triangular planes.
IGES (or IGS):
- File extension: .iges, igs
- Type: Neutral
IGES (lnitialGraphics Exchange Specification) is a standard file format for CAD data exchange. Its original intention was to create an intermediate format that could exchange complex 3D data (including lines, curves, surfaces, and solids) between various CAD software. As for IGS, it is the file extension of IGES format. In other words, when you see a CAD file with an “igs” extension, it actually follows the IGES specification.
STEP:
- File extension: .stp, .step
- Type: Neutral
STEP provides a comprehensive approach for CAD data exchange, supporting geometric, component, assembly, material, and texture information. Compared to IGES, STEP provides more complete data support. When using STEP, it is necessary to ensure that the target system supports all relevant STEP subsets.
PDF:
- File extension: .pdf
- Type: Neutral
Although PDF is primarily a document format, 3D PDF is capable of embedding 3D models. Models can be viewed in standard PDF readers but may not contain all raw data such as metadata.
X3D:
- File extension: .x3d
- Type: Neutral
X3D (Extensible 3D) has become the successor of VRML in the field of web-based 3D graphics, mainly used for 3D graphics display. It supports textures, materials, and animation, but may not have some advanced CAD-specific features. Additionally, it is very useful in interactive 3D scenes and network 3D applications.
ACIS-SAT (or SAT)
- File extension: .sat, .sab
- Type: Kernel
ACIS-SAT is a file format designed specifically for 3D modeling applications. It can contain complex geometric data, model properties, and application-specific information. Compatibility is an important consideration when exchanging these files with other CAD systems. Plus, the ACIS-SAT format supports two extensions: SAT (Standard ACIS Text), which is human-readable and allows manual adjustment of model content; and SAB (Standard ACIS Binary), which is more compact, safer, and does not cause round-off errors.
JT:
- File extension: .jt
- Type: Neutral
As a format for Siemens PLM Software, JT provides a lightweight 3D data exchange method supporting 3D geometric components and assemblies. Also, JT is useful when exchanging data between multiple PLM systems.
VRML:
- File extension: .wrl, .wrz
- Type: Neutral
VRML (Virtual Reality Modeling Language), similar to X3D, is a 3D graphic description language that can be used to create three-dimensional representations and objects of complex scenes, supporting materials, textures, and animations. Its usage scenarios were mainly in early 3D network applications, and it has been gradually replaced by X3D.
Parasolid-XT
- File extension: .x_t, .x_b, .xmt_txt, .xmt_bin, .xmp_txt, .xmp_bin
- Type: Kernel
Parasolid-XT is another persistent format that is part of the modeling kernel. This is a file format specifically designed to represent complex 3D geometry, which may not support textures or metadata but performs well in high-precision modeling.
SLDPRT
- File extension: .sldprt
- Type: Native
SLDPRT is a native file of SolidWorks that captures all aspects of the model, such as materials, textures, application-specific data, and history. It also helps protect intellectual property because it allows you to share only the necessary parts of your system with collaborators. Therefore, conversion may be required when sharing files with non-SolidWorks users.
CATPar
- File extension: .sldprt
- Type: Native
CATpart is a 3D graphics format designed by CATIA software, very similar to SLDPRT. It is optimized for advanced engineering design and integrates rich geometric, material, and application-specific data, mainly used in car manufacturers, aerospace, and other fields.
When using these CAD file formats, it is always important to consider end-use and compatibility. Ensure the appropriate software version is in place and perform necessary file validation to guarantee data integrity and accuracy.
Choosing the Right CAD File Format: A Quick Overview
“Which CAD file format should I use?”
To help you solve this problem, we provided you with a detailed introduction to 15 commonly used CAD file formats in the previous section. Besides, we will next display information on each format in the form of a table so that you can learn about the most suitable one quickly.
| CAD File Format | Software Compatibility
|
Conversion Compatibility | Use
|
Storing Properties | Type | 2D/3D |
| DWG | AutoCAD and most CAD software
|
Relatively High | Architecture, mechanical design, etc | Geometry, Topology, Product Design, Meta-Data, Visual Representation of Qualities | Native
|
2D & 3D |
| DXF | Most CAD software | High | Data exchange
|
Geometry, Topology, Product Design, Meta-Data | Neutral | 2D & 3D |
| STL | Most 3D printing programs and CAD software | Medium | 3D printing | Geometry | Neutral | 3D |
| IGES or IGS | Most CAD software
|
High | Data exchange | Geometry, Topology, Product Design, Meta-Data | Neutral | 2D & 3D |
| STEP | Most CAD software | High | Data exchange | Geometry, Topology, Product Design, Meta-Data, Visual Representation of Qualities | Neutral | 2D & 3D |
| Most software | Medium | Display, printing | Geometry, Visual Representation of Qualities | Neutral | 2D & 3D | |
| X3D | Most web 3D software | Medium | Web display
|
Geometry, Visual Representation of Qualities | Neutral | 3D |
| ACIS-SAT or SAT | SpaceClaim and most CAD software | Medium | 3D design | Geometry, Topology, Product Design, Meta-Data, Visual Representation of Qualities | Native | 3D |
| JT | Siemens PLM and most CAD software | Medium | Data exchange, PLM | Geometry, Topology, Product Design, Meta-Data, Visual Representation of Qualities | Neutral | 2D & 3D |
| VRML | Most web 3D software | Medium | Web display | Geometry, Visual Representation of Qualities | Neutral | 3D |
| Parasolid-XT | NX, Solid Edge, and most CAD software | Medium | 3D design | Geometry, Topology, Product Design, Meta-Data, Visual Representation of Qualities | Native | 3D |
| SLDPRT | SolidWorks | Medium | 3D design, mechanical part | Geometry, Topology, Product Design, Meta-Data, Visual Representation of Qualities | Native | 3D |
| CATPar | CATIA | Medium | 3D design, mechanical part | Geometry, Topology, Product Design, Meta-Data, Visual Representation of Qualities | Native | 3D |
How to Open a CAD File
When co-processing a CAD file, you may encounter situations where you cannot open the CAD file shared by others. This is because the CAD software and file format are incompatible. Moreover, some CAD software versions may not be able to open new versions of CAD files if they are older. However, if you use professional CAD software such as AutoCAD and ZWCAD, then almost all CAD files can be opened smoothly. Next, we will take ZWCAD as an example to introduce how to open CAD files.
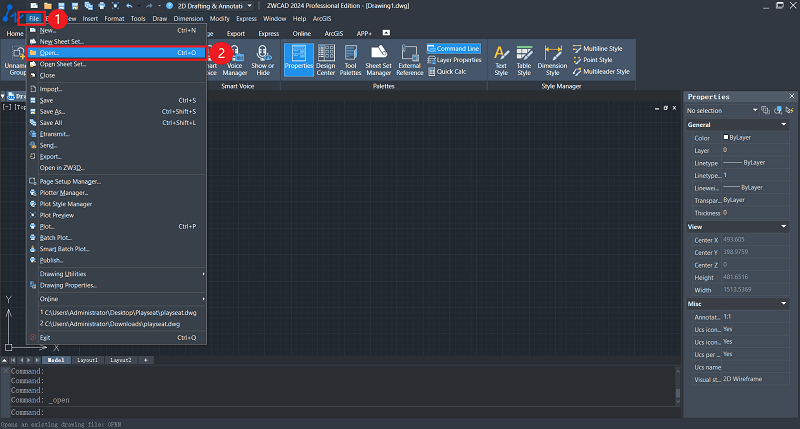
Step 1. Launch ZWCAD software.
Step 2. Click on “File” in the upper menu, then select “Open”.
Step 3. Browse the location of your target CAD file and open it. Or, you can double-click on the CAD file. If ZWCAD is already installed on your computer, it will automatically open.
Note:
ZWSOFT has released ZWCAD Flex, a subscription-based CAD solution currently available exclusively in the United States and Canada.
Users outside these regions are encouraged to contact their local ZWSOFT sales team to explore perpetual license options for ZWCAD.
FAQs About CAD File Formats
What File Formats Can AutoCAD Export?
AutoCAD supports multiple CAD file formats for export for different purposes such as 3D printing, 3D modeling, design viewer, data exchange, etc. The most commonly used CAD file formats are DWG, DXF, PDF, DWF, BMP, JPG, PNG, TIFF, STL, FBX, STEP, and IGES.
Additionally, there are some other specific export options for AutoCAD, but the ones listed above are the most common. Different AutoCAD versions and configurations may have different outcomes. Here are some supported formats that are rarely used: DGN, TGA (TARGA), WMF (Windows Metafile), EPS (Encapsulated PostScript), SVG, OBJ, and 3DS.
How to Open .dwg File Without CAD Software?
The most straightforward method is to use online viewers like AutoCAD for Web, a web-based online viewer that enables users to access, design, and update DWG files with a familiar AutoCAD-like interface. It requires no installation. No matter where you are, you can directly access it to have a quick collaboration with AutoCAD users on designs.
How to Convert PDF to CAD File?
You can try to use online tools to convert, but this method will require you to upload your files to the website. For security reasons, we recommend using CAD software that supports PDFs, such as ZWCAD, for conversion. First, you can open the PDF file in ZWCAD software, and then use its built-in format conversion function to select the desired output format such as DWG to convert it into a CAD file.
Conclusion
When it comes to turning imaginative ideas into tangible designs, CAD file is incredibly useful. However, it’s crucial to choose the right CAD file format for your design. In this article, we have introduced you to the 15 most commonly used CAD file formats, so you can quickly determine the most suitable option. We also shared more information about CAD file formats to help you in the future. If you find this article helpful, please share it with others who may benefit.
.png)