As a companion tool for 3D printing, also known as subtractive manufacturing, 3D printers can convert CAD models into physical objects. From complex prototypes and components to everyday consumer goods, many things can be made on 3D printers. It’s safe to say that 3D printers have a broad future and are also changing the manufacturing methods of various industries.
But have you ever figured out the question of how does a 3D printer work? Its principle can make your business more adaptable to 3D printing, driving more innovation and faster efficiency. More importantly, this knowledge helps you quickly troubleshoot issues when they arise. If you have only put a 3D printer into practice without delving into its workings, this article is a good start. Starting with the types of 3D printers, taking FDM 3D printers as an example, this post will explain how general 3D printers work. Let’s dive in!
| Note: If you need to adjust and optimize your model such as adjusting the printing parameters and adding supports before 3D printing, you can try ZW3D. This is a beginner-friendly 3D solution that works stably and smoothly. Lately the ZW3D 2025 version has been released and you can download it. If you are looking for the best 3D modeling software, don’t miss it. |
What Are the Types of 3D Printers?
3D printers are not one-size-fits-all device. There are many variations based on different printing technologies and materials. Following FDM, SLA, and SLS are common types of printing equipment used in various industries.
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
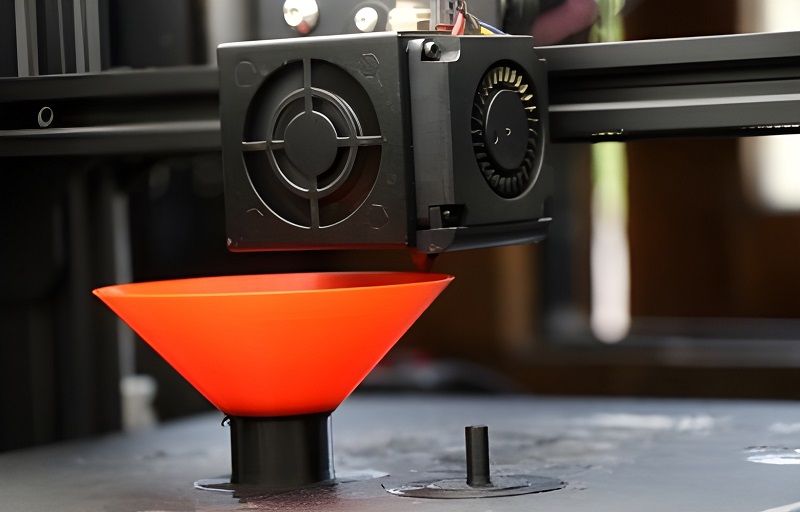
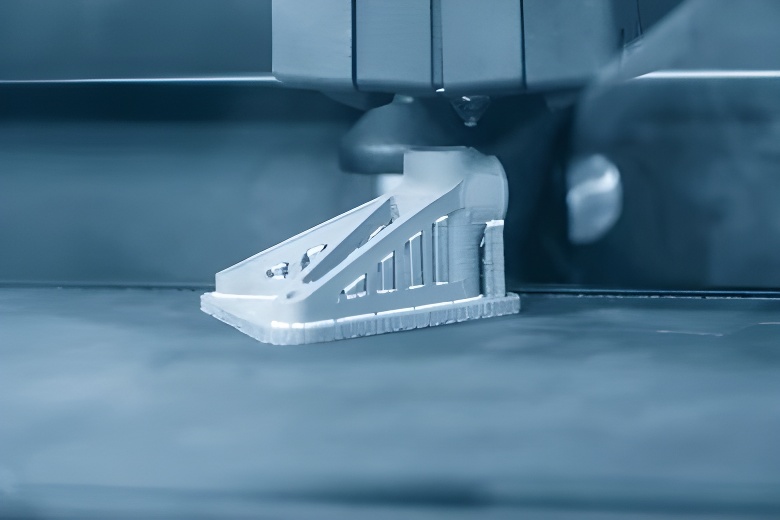
FDM, or FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication), is a 3D printing technology that uses thermoplastic filaments such as PLA, ABS, and PETG as the main material. Such filaments are heated to their melting point, extruded through a nozzle, and deposited layer by layer on the printing bed to form a three-dimensional object. Because of easy-to-grasp materials and operation, FDM 3D printers are considered an entry-level and commonly used type of printer.
Currently, FDM 3D printers are widely used in fields such as prototyping, manufacturing, design, and education. Especially in prototyping, they can create physical models at a relatively low cost, allowing designers and engineers to iterate before mass production. However, since this type of printer forms objects by stacking layers, slightly improper operation will cause obvious ripples on the printed object surface.
SLA (Stereolithography)
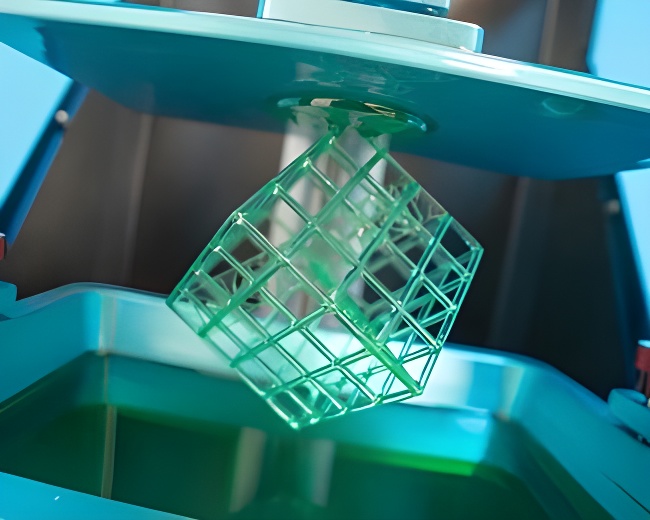
SLA 3D printers can be traced back to the 1980s when SLA technology was invented. Unlike FDM, SLA uses ultraviolet lasers or DLP projectors to cure liquid photopolymer resin layer by layer to print objects. Due to the materials used, SLA printers are also referred to as resin 3D printers. This printing equipment typically consists of several main components: a laser or DLP projector, a resin vat, a build platform, and a scanning system (only for laser SLA devices). The overall setup is relatively complex.
As a result, you will often see questions on various platforms about how does a resin 3D printer work. However, if operated skillfully, the printed object will have smooth surfaces without wrinkles. In this case, SLA 3D printers are better suited for precision parts and complex models. Many 3D printers for dental, jewelry, and healthcare applications have emerged.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
If you work in industrial fields such as aerospace, medical devices, or automotive parts, you might be familiar with Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Printing types of equipment that use this technology are known as SLS 3D printers. Since they typically use CO2 lasers to process materials, you might also come across them when searching for laser 3D printers online. So how does a laser 3D printer work?
In simple terms, powders of materials such as plastic, metal, ceramic, or nylon are poured into a powder bed. Then this type of 3D printer will use a high-power laser to sinter the powder layer by layer into solid objects according to the preset model and settings. Thanks to powder materials that can support uncured parts, complex structures can be printed directly without additional support. Moreover, objects produced by SLS 3D printers are highly accurate and more durable. But this also comes with advanced processing skills and a higher budget.
How Does a FDM 3D Printer Work When 3D Printing?
Now let’s take a deep dive into how a 3D printer works. This will give you the confidence to produce high-quality physical objects when you start 3D printing. Given that FDM is the most common and its learning curve is not steep, here will take it as an example to explain in detail.
1. Control System Receives Instructions
Every FDM 3D printer is equipped with a control system, which is the core component to receive instructions, translate them into actions, and monitor the printing process. Although it varies depending on the printer itself, it generally consists of a microcontroller and drivers. As the CPU of the entire system, they will receive printing parameters set by the slicer, such as speed, wall thickness, infill percentage, and layer height, and send commands to the other components, ensuring that the printer can work according to the established path.
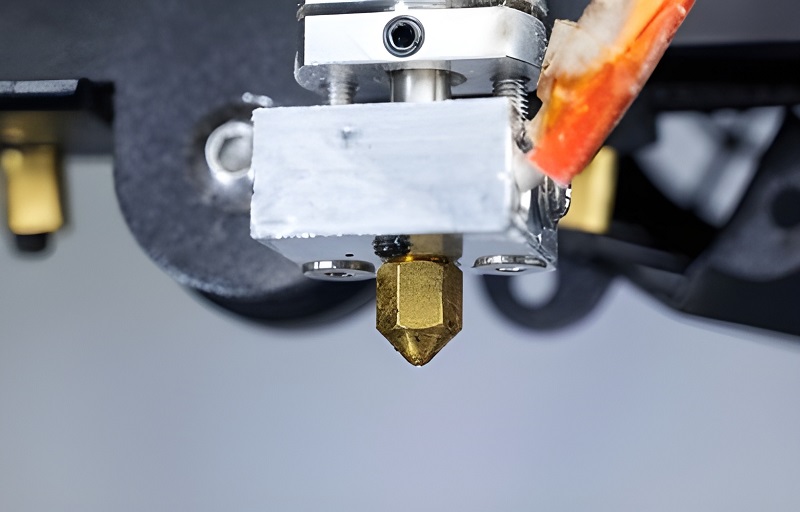
2. Extruder Prepares Filament
Now it’s time for the extruder to work. The FDM 3D printer extruder also operates under the guidance of the control system. Following G-code instructions, the microcontroller specifies the amount of filament needed for each layer. The temperature controller receives the target temperature required to heat the filament from the microcontroller and maintains it with the help of the heating element.
At this time, a component called a thermistor sensor embedded in the nozzle is also playing a role. The temperature it monitors will lead the temperature controller to adjust the power and ensure consistent heating of all filaments. If your FDM 3D printer is more advanced, it may also have a filament sensor. This sensor can detect when the filament is running out or clogged, allowing you to promptly replenish or clear the printing material.
3. Motion System Positions Print Head
Typically composed of stepper (linear) motors, belts, pulleys, and other parts, the motion system in an FDM 3D printer helps the nozzle move precisely along the X, Y, and Z axes to deposit the filament layer by layer onto the printing bed. This movement is also directed by the G-code, and the nozzle is usually positioned at the edge or corner of the printing bed first to ensure accurate printing.
Notably, FDM 3D printer motion systems come in three different configurations: Cartesian, CoreXY, and Delta systems. The Cartesian system is the most common and cost-effective, but it may wobble or vibrate in fast printing. The CoreXY System uses a fixed bed and a moving extruder to reduce vibration but requires high-quality belts. As for the Delta System, it uses a triangular frame, helpful for high-speed printing, but it may struggle with precise small details.
4. Printing Begins
When an FDM 3D printer starts a printing job, the control system sends instructions, and the drive gears, heating elements, and thermistor sensors in the extrusion system work to melt and extrude the filament. Simultaneously, components in the motion system will also join efforts to ensure accurate printing.
At this stage, besides focusing on figuring out how a 3D printer works when printing items, you should also pay attention to practical operations to avoid printing errors. The distance between the nozzle and the print bed needs to be tested and adjusted in advance to achieve the best printing effect. Depending on the material and model requirements, the print bed also needs to be heated to improve the adhesion of the first layer. Most importantly, all printing operations should be carried out in line with the equipment instructions to avoid unnecessary damage to the printer.
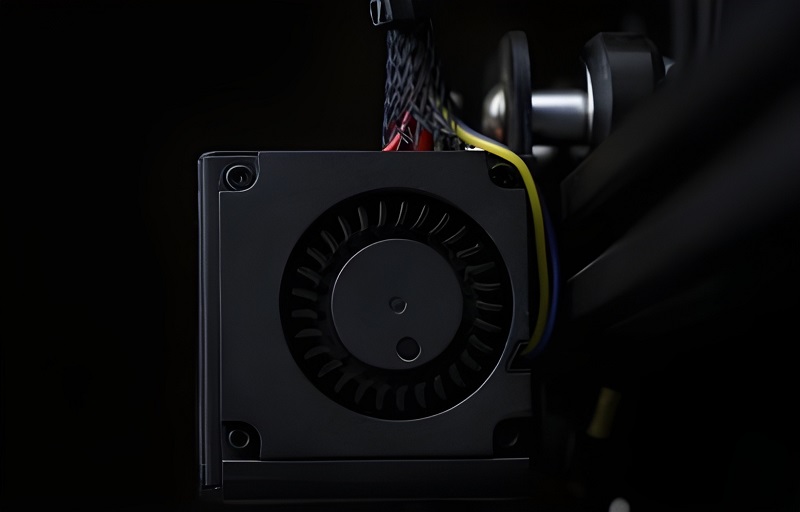
5. Filament Cooling and Curing
FDM 3D printers generally feature one or more cooling fans near the extruder nozzle to cool and solidify the filament. These cooling fans can help the filament solidify faster, reduce drooping or warping, and thus achieve clearer features and cleaner print quality. In addition, cooling fans are beneficial for rapid prototyping, even if your printed object is unsupported.
Beyond that, there is an extra tool called a 3D printing raft that can also aid in filament and model cure. It’s a horizontal lattice-like structure between the printed part and the print bed. If the print raft is not set evenly or does not work well, it may cause the entire print to warp or detach, affecting the final print quality.
6. Repetition of Printing Until Completion
Whether it’s an FDM, SLA, or SLS 3D printer, they all involve layer-by-layer printing and cooling of materials. Therefore, when the deposition and cure of one layer of filament is completed, the control system will send commands for the next layer in G-code format to re-coordinate the extruder and motion system. This will ensure that each layer is printed smoothly and accurately. It’s important to note that while cooling fans are active throughout the process, they are suggested to be turned off or set to low speed to improve bed adhesion for the first layer.
FAQs About 3D Printer
How to Maintain and Upkeep a 3D Printer?
The stable performance and long lifespan of a 3D printer rely on regular maintenance. Here are some detailed upkeep tips:
- Component Cleaning: Clean the 3D printer after every use. Additionally, routinely clean the print bed, nozzle, and other components to prevent clogs and malfunctions;
- Device Maintenance: Inspect the printer’s electronic components, motors, connectors, and other parts every one to two weeks. Timely detection and repair of potential issues can prevent equipment damage;
- Nozzle Replacement: Replace worn nozzles to ensure smooth filament flow and adhesion. The printing materials also need to be selected during use to find the best match for the 3D printer;
- Software and Firmware Updates: Regularly check and update the software and firmware of the 3D printer. This helps it recognize and analyze printing commands and optimize performance;
- Maintain Ventilation: Store the 3D printer in a well-ventilated environment, which can quickly dissipate heat and odors generated during printing;
- Follow Product Instructions: Carefully read the maintenance guidelines by the manufacturer. Different brands and models of 3D printers may vary in this, so be sure to refer to them as a guide.
How to Choose the Right 3D Printer?
Choosing the right 3D printer depends on your needs and priorities. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Printing Needs: Determine the type and size of the objects you intend to print. Based on this, consider whether you need a 3D printer with some advanced features;
- Ease of Use: If you are a beginner, it’s recommended to choose a 3D printer with a user-friendly interface and easy setup. Alternatively, opt for products that come with comprehensive guidance;
- Budget: Consider the cost of the printer as well as the subsequent maintenance costs. Choosing within a reasonable budget will reduce the pressure on the return on investment;
- Printing Materials: Select based on the materials required for your project. PLA and ABS are suitable for FDM 3D printers, while nylon, glass, and metal are better for SLS printers;
- Brand Reputation: Choose a reputable and reliable manufacturer. This is beneficial for the long-term use of the 3D printer and for after-sales service;
- Community Support: Check if the chosen 3D printer has an active community. This can help you with comprehensive reviews and problem-solving during use.
Conclusion
In summary, the principles of a 3D printer are closely related to its structure, components, and printing materials. Its basic working method is traceable, but the specific operation will vary depending on the brand and model. Therefore, the answer to the question of how does a 3D printer work is often given based on the different types of 3D printers. Detailed instructions and data still need to come from the manufacturer. If you want to learn more about different 3D printers, start with this post and try a model yourself. First-hand experience and data are more convincing than existing text.
.png)