When working on 3D projects, choosing the right file format is essential to prevent compatibility problems and data loss. The best format depends on how you intend to use your 3D model. For example, a format compatible with your 3D printer is crucial for printing, while for engineering design, it is important to use formats that maintain precise geometry and support detailed technical data.
If you find it challenging to make the decision, this article explores the 9 most common 3D file formats to help you choose the best option for your project. Let’s learn more now!
Contents
- 1. What Are 3D Files? What Are the Types of Them?
- 2. Classification by Format Ownership
- 3. Classification by Use Case or Industry
- 4. The 9 Most Common Neutral 3D File Formats
- 5. FAQ About 3D File Formats
- 6. Conclusion
| Related Article: |
What Are 3D Files? What Are the Types of Them?
3D files are used to store 3D model data, which contains information such as the model’s geometric shape, texture, material, animation, lighting, and scene. This enables models to be displayed, edited, and rendered in computer graphics software.
These files are usually created by dedicated 3D modeling software and are widely used in engineering design, 3D printing, video games, film production, etc. Common 3D file formats include STL, OBJ, FBX, etc., each with its own features and special uses.
Additionally, 3D file formats can also be categorized in two main ways:
- By file format ownership (proprietary vs. neutral)
- By industry or use case (modeling, printing, gaming, etc.)
Classification by Format Ownership
Proprietary 3D File Formats
Proprietary 3D file formats are developed and used by specific software programs or companies. For example, .max for Autodesk 3ds Max, .c4d for Maxon Cinema 4D, and .blend for Blender.
| File Format | Software | Use Description |
|---|---|---|
| .max | Autodesk 3ds Max | Advanced modeling, rendering, animation |
| .mb / .ma | Autodesk Maya | Animation, VFX, character rigging |
| .z3prt / .z3asm / .z3drw | ZW3D | Used for part design, assembly design, and 2D drawing |
| .sldprt, .sldasm | SolidWorks | CAD parts and assemblies |
| .prt, .asm | PTC Creo (Pro/ENGINEER) | Engineering design and manufacturing |
| .blend | Blender | Open-source modeling, animation, simulation |
| .c4d | Maxon Cinema 4D | Motion graphics and animation for film/ads |
| .skp | SketchUp | Architectural and interior design |
| .x_t / .x_b | Siemens NX / Solid Edge (Parasolid) | High-precision CAD modeling |
| .ipt, .iam | Autodesk Inventor | Part and assembly design |
| .3dm | Rhino (McNeel) | Industrial, architectural, and jewelry design |
| .lwo | LightWave 3D | Legacy animation and modeling software |
| .zpr | ZBrush | High-detail sculpting and painting |
| .dgn | Bentley MicroStation | CAD for infrastructure and construction |
These formats fully utilize the native features of the software, offering optimized workflows. However, their compatibility with other programs is limited. For example, .blend files cannot be opened directly in Autodesk 3ds Max.
Neutral 3D CAD File Formats
Neutral 3D CAD file formats are open or standardized formats that can be used across different platforms and applications. They offer greater compatibility but may not support advanced features unique to proprietary formats. Common examples include .stl, .obj, and .fbx.
Classification by Use Case or Industry
3D files can also be grouped based on their primary application. This helps users choose the most suitable format depending on their workflow needs.
3D Modeling and Animation
These formats are widely used in computer graphics, film, and architecture for creating detailed models with materials, textures, and animation data
- OBJ (.obj) – Geometry and texture; highly compatible.
- FBX (.fbx) – Rich support for animation and scene data.
- DAE (.dae) – Interchange format for models with hierarchy and animation.
- BLEND (.blend) – Native Blender format for full project files.
3D Printing
Focused on geometry and manufacturability, these formats are optimized for slice-based additive manufacturing.
- STL (.stl) – Simplified mesh, no color or texture.
- 3MF (.3mf) – Next-gen format with color/material support.
- AMF (.amf) – XML-based, extensible format with advanced features.
Gaming and Real-Time Rendering
Used in game engines and AR/VR environments, these formats are optimized for performance and interactivity.
- GLTF/GLB (.gltf / .glb) – Web and mobile-friendly real-time format.
- FBX (.fbx) – Widely supported in Unity and Unreal Engine.
- DAE (.dae) – Also used in game pipelines with good interoperability.
The 9 Most Common Neutral 3D File Formats
Choosing a proper 3D file format is crucial for your 3D project. Here’s a detailed overview of the 9 most common neutral 3D file formats, delivering their strengths and weaknesses to help you pick the right one quickly.
1. STL
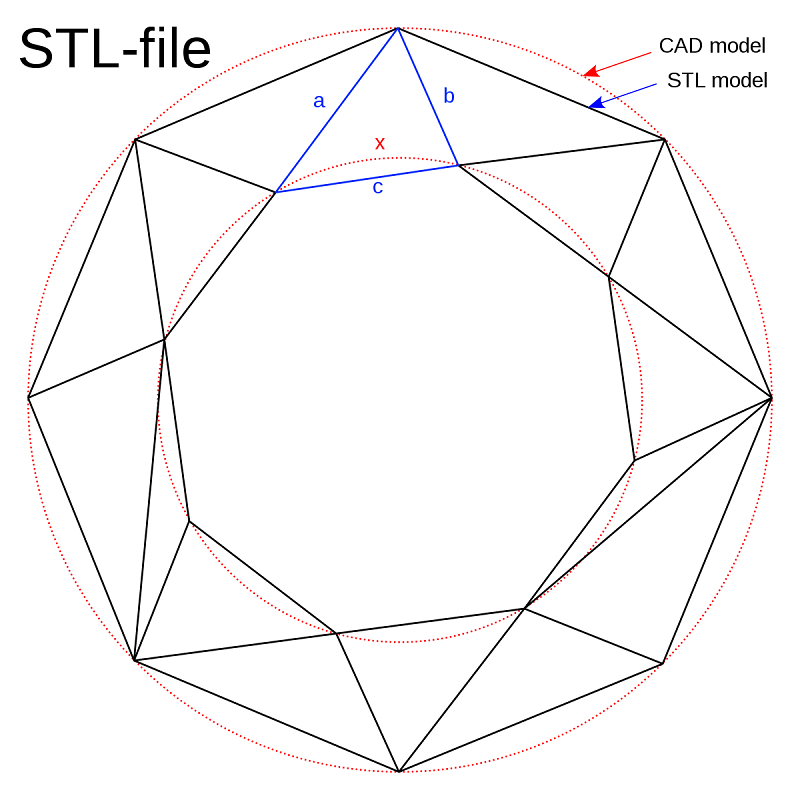
STL is a universal 3D file format used to store 3D surface geometry data. It uses triangle meshes as basic units to represent the model surface, effectively describing its shape and contour. Also, it’s popular in 3D printing and CAD software due to its simplicity, ease of use, and strong versatility.
Pros
- Offer 3D printing format files supported by almost all 3D printers and CAD software.
- Provide efficient storage with relatively smaller files in size.
- Provide faster processing speed than other files.
Cons
- Lack of material, texture, color, and other detailed data.
- Lose detail and smoothness in the model’s surfaces as STL files use triangle meshes.
2. OBJ
Another universal 3D file format is OBJ, which is widely supported by mainstream 3D software. It contains details about a model’s geometry, texture, and material. In addition, OBJ files use a text-based format for data storage, which can be directly opened with a text editor for viewing and editing.
Pros
- Compatible with almost all 3D model software for easy sharing and collaboration.
- Contain all model information, suitable for complex 3D models.
Cons
- Present larger files in size, not ideal for storing large projects.
- Offer less efficiency in editing OBJ files due to the text-based format.
3. FBX
FBX, a proprietary 3D model file format developed by Autodesk, supports a wide range of 3D modeling data, including geometry, textures, materials, animations, lighting, and scenes. Moreover, it also contains animation data, making it ideal for meeting the needs of various complex 3D models in gaming, film, VFX, and animation production.
Pros
- Work with various 3D model software and game engines.
- Store detailed model information, ideal for game development and animation production.
Cons
- A proprietary 3D file format, along with potential incompatibility issues.
- Deliver a large file size with a slow storing speed.
4. COLLADA
COLLADA is an XML format file developed by Khronos Group that is designed to store 3D scene data, including geometry, textures, materials, animations, and even entire scenes. Moreover, it utilizes the .dae extension (Digital Asset Exchange), facilitating data exchange among various software. This makes COLLADA files widely used in 3D game development, 3D film and television production, 3D design and engineering, virtual reality and augmented reality, and other fields.
Pros
- Open standard 3D file format for various data storage.
- Ideal for data exchange among different software.
Cons
- Large and difficult to edit for some projects.
- Offer a slow processing speed.
5. 3DS
3DS, developed by Autodesk, is a 3D drawing file format primarily used in 3D Studio Max software. It can store detailed 3D model data, including camera position, viewport configuration, animation information, and so on. Despite it has platform limitations, 3DS is known for its image quality and detailed features, making it a valuable option in various fields, such as production, engineering, and architecture.
Pros
- Offer lightweight 3D files, suitable for quick transfer.
- An industry standard file format for storing 3D graphic information.
Cons
- A proprietary 3D file format with low compatibility.
- Lack of advanced features like tangent information.
6. IGES
IGES is a neutral 3D file format developed by the National Bureau of Standards (NBS) in 1980, facilitating the exchange of 2D and 3D information between different CAD software.
As a text-based format that uses ASCII code to represent data, IGES offers strong readability and editability and is convenient for manual inspection and modification. This makes IGES files popular among producers and designers who need to plan, price, and specify the details of construction and design projects.
Pros
- Serve as a neutral 3D CAD file format used for data exchange among different CAD software.
- Support complex geometric structures such as surfaces and topologies.
- Small and easy to share.
Cons
- Outdated 3D file format with limited features.
- Not ideal for handling large projects.
7. 3MF
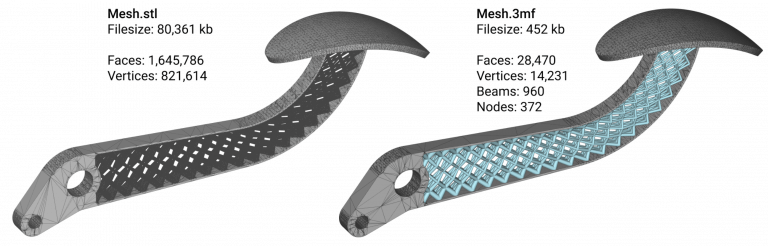
3MF is a file format designed for 3D printing, jointly developed by leading companies such as Microsoft, Autodesk, and 3D Systems in 2015. It offers richer functions and features, including definitions of colors, materials, and precise shapes that do not exist in STL files.
This enables the 3MF file format to describe 3D models more accurately and provide richer functionality for 3D printing. If you are looking for a file type for 3D printing, 3MF is one of the options.
Pros
- Offer dedicated 3D printing format file.
- Suitable for storing and exchanging 3D printing data.
Cons
- Not widely supported by all 3D printing software, especially old devices.
8. STEP
STEP is an open-standard file format specifically designed for exchanging and storing product data. Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), it facilitates seamless data exchange and sharing between different CAD, CAM, and CAE software.
Additionally, STEP files can store all information about 3D models, including geometry, dimensions, tolerances, materials, colors, textures, assembly relationships, etc. This enables them to fully describe the product models, providing a foundation for effective data management and collaboration across all stages of product development.
Pros
- Benefit data sharing and collaboration between different CAD, CAM, and CAE software.
- Universal 3D file format for various software.
Cons
- Take a lot of time to create a STEP file due to its complexity.
- Potential compatibility issues with some software.
9. VRML
VRML is a 3D file format used for displaying interactive 3D graphics and virtual reality scenes. It provides a standardized data format for virtual reality applications across the web. VRML files support a variety of data types, including 3D models, textures, lighting, animations, and even interactive elements.
While VRML97 has been utilized on some personal pages and 3D chat sites, it has not been widely adopted. Moreover, X3D, the successor to VRML, was released in 2001 and gradually took its place.
Pros
- Standard file format for storing 3D graphics and virtual reality scenes.
- Supports a variety of data, such as geometry, animation, interaction, etc.
Cons
- Outdated 3D file format with a narrow range of applications.
- Unable to work properly in some software.
FAQ About 3D File Formats
How to Select the Appropriate 3D Format for Your 3D Project?
When choosing the right 3D file format, determine the functions and features required for the project first. For example, if your model is used for 3D printing, you may need to use a 3D printer file format.
Next, opt for a format that is compatible with the 3D modeling software you use. While popular 3D software programs like 3ds Max, Maya, and ZW3D support multiple formats, some proprietary 3D file formats may have compatibility issues.
Additionally, file size is also a factor to consider. Some formats may produce larger file sizes, while others can compress and store 3D data more efficiently, reducing file sizes. If you are a beginner and have no idea which format to choose, it is recommended to start with universal 3D file formats, such as STL or OBJ.
| NOTE: In the latest ZW3D 2026, the upgraded IPX 2.0 engine enables accurate feature-level data exchange with major CAD formats, achieving over 90% conversion accuracy for SolidWorks files and 85% for Creo files. This ensures smooth collaboration across multi-CAD environments. If you’re interested, you can download a free 30-day trial to experience it for yourself. |
Which Is the Best File Type for 3D Printing?
When it comes to the best 3D printer file format, STL stands out as the best option. STL is a widely used 3D printing file format that can be recognized and read by almost all 3D printers. It is also compatible with most 3D modeling software, allowing for straightforward export of your models for printing. This helps simplify the 3D printing workflow and improves efficiency.
Another advantage of STL is its simplicity and efficiency. Compared to other 3D file formats, STL files only store essential geometric data, resulting in compact file sizes and ease of processing. This greatly facilitates faster printing and less storage requirements. Therefore, if you are looking for a user-friendly file type for 3D printing, STL is an excellent choice.
Conclusion
This article introduces the 9 most common 3D file formats, including STL, OBJ, FBX, COLLADA, 3DS, IGES, 3MF, STEP, and VRML, with pros and cons to help you make better choices that suit your project.
Apart from choosing the right format, it is also crucial to use the right 3D modeling software when working on 3D projects. ZW3D is a great option. It is an easy-to-use and powerful 3D modeling software that supports all popular 3D modeling file formats, providing users with an efficient and innovative design experience.
If you find this article helpful, please share it to spread knowledge and let more people get helped!