While CAD and BIM have something in common, some people may fix up with them. Actually, both of them are used in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. Still, they focus on different aspects like the scope, workflow, information management, rendering capability, design visualization, collaboration, etc. To walk you through the differences, let’s compare BIM vs CAD in their usage, silver linings, and drawbacks through this guide. You will make the right choice afterward.
What Is CAD?
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) refers to the use of software tools to create, modify, analyze, and optimize designs. CAD software enables designers to create detailed two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) models of objects or systems.
The history of CAD dates back to the early 1960s when the first efforts were made to develop computer systems that could assist in design tasks. During the 1970s, advancements in hardware technology, such as the introduction of minicomputers and graphics terminals, made CAD systems more accessible. In subsequent years, CAD systems evolved rapidly while incorporating 3D modeling capabilities, parametric design, and improved visualization tools.
Today, CAD has its importance in civil engineering, architecture, and manufacturing. The CAD software is extensively used in various industries for designing buildings, products, and infrastructure. It continues to evolve, incorporating new technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to enhance the design and visualization experience.
What Is BIM?
BIM (Building Information Modeling) is a process that involves creating and managing digital representations of a building’s physical and functional characteristics. It goes beyond just geometry and includes additional information about the building’s components, materials, properties, relationships, and more. It enables a more integrated and efficient approach to design, construction, and maintenance throughout the entire lifecycle of a project.
The history of BIM can be traced back to the 1970s and 1980s when early CAD systems were being developed. However, the true origins of BIM as we know it today can be attributed to the work of Charles Eastman and his team in the late 1990s. At the time, they developed a software called GABLES (Georgia Tech Automated Building, Layout, Evaluation, and Simulation) that introduced the concept of object-based modeling. In 1999, the term “Building Information Model” first came into the public.
Over time, BIM gained traction and was widely adopted in architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries. As technology advanced, BIM evolved to incorporate more sophisticated features like interoperability, cloud collaboration, and integrated analysis tools. Today, BIM plays a critical role in the construction industry that allows designers to visualize, simulate, and analyze the building process from concept to operation.
BIM vs CAD: What are They Used for?
BIM (Building Information Modeling) and CAD (Computer-Aided Design) are both widely used in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries. While sharing some similarities, they serve different purposes.
CAD is primarily used for creating 2D or 3D digital designs that allow architects, engineers, and designers to create precise drawings, draft plans, and generate technical documentation. Architectural CAD software provides tools for creating, editing, and manipulating objects, lines, curves, and surfaces. It is used for detailed design work, such as architectural layouts, mechanical drawings, structural analysis, and manufacturing designs. Meanwhile, it’s applicable to more usages like.
- Drafting and Sketching: CAD is widely used for creating engineering drawings, such as floor plans, profiles, and elevations.
- Product Design: CAD is used in engineering and product design, including mechanical, electronic, and architectural fields.
- Mechanical Manufacturing: CAD is utilized in manufacturing engineering, such as for part design and the formulation of machining processes.
On the other hand, BIM goes beyond traditional CAD by incorporating not only geometric representation but also intelligent data and information about various aspects of a building or infrastructure project. BIM models contain not just the visual representation of components but also their properties, relationships, and behavior throughout the project lifecycle. Moreover, BIM is mainly used for the following purposes.
- Design and Planning: BIM enables designers to create highly detailed architectural models, providing better visualization of projects and the ability to identify potential issues.
- Collaboration: Team members can share BIM models as well as improve collaboration and information sharing, thereby enhancing project efficiency and quality.
- Quantification and Budgeting: BIM can automatically generate material lists and cost estimates that help project managers better understand budgeting.
- Maintenance and Management: BIM models can be utilized for the maintenance and management of buildings, including equipment maintenance and updates.
While comparing CAD vs BIM, CAD focuses more on drawing and product design. On the other hand, BIM is mainly used for the entire lifecycle management of architectural and engineering projects, including design, construction, maintenance, and management. According to project needs, one can choose to use BIM, CAD, or a combination of both for optimal results.
BIM vs CAD: Advantages and Disadvantages
| CAD | BIM | |
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantage |
|
|
While the benefits of CAD and BIM are appealing, it is important to address their disadvantages and challenges to fully leverage their potential in the design process. Furthermore, let’s take a look at the quick comparison between CAD vs BIM below.
BIM vs CAD: A Quick Comparison
| CAD | BIM | |
| Dimension | 2D, 3D | 2D, 3D |
| 3D Rendering | Primary rendering capabilities | Enhanced rendering capabilities for realistic visualizations |
| Information Management | Mainly handle graphical data like 2D drawing and 3D modeling
|
Use for lifecycle management of the entire construction project, including integration and management of 4D, 5D, 6D, and 7D information |
| Design Visualization | Simple and basic
|
More advanced which reduces design errors and conflicts |
| Collaboration | Limited collaboration features | Strong collaboration features, aiding multi-disciplinary teamwork |
| Workflow | Require manual workflow management | Integrated workflow management to optimize processes |
| Learning Curve | Comparatively easy to learn | Hard to learn |
| Applications
|
Mainly used for drawing and design in many industries such as mechanical design, electronic and electrical design, civil engineering, architectural drawing, cartography, and graphic design | More suitable for integrated construction projects and full lifecycle management, such as architectural design and engineering, facilities management, land planning, industrial design, sustainable design |
This comparison table will show you the overall differences between CAD and BIM in various aspects. Simply put, BIM has better features in rendering, workflow, and collaboration while CAD is more easy to learn and is applicable to a wider range of industries.
Tips: Best CAD and BIM Software You Should Know
If you’re in need of CAD or BIM software, you may consider a suitable choice according to your proficiency, project requirements, and individual preferences. To save your time shopping around, here introduce the best CAD software and BIM software for you.
Best CAD Software: ZWCAD
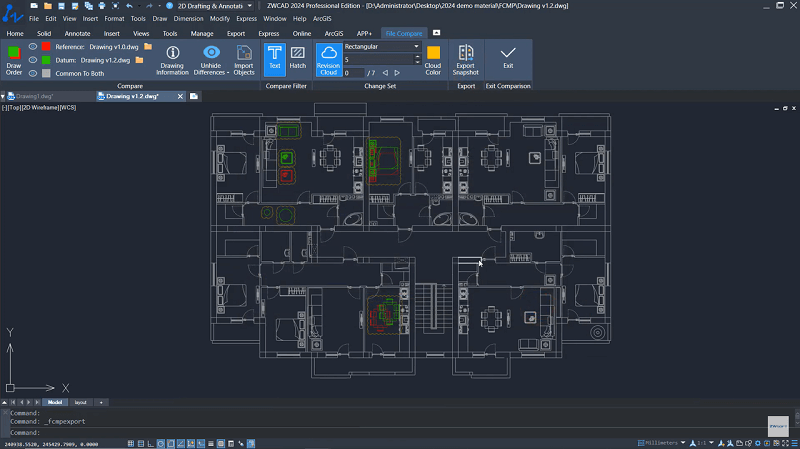
ZWCAD is the optimal solution for a wide range of industries that enables both beginners and professionals to quickly create 2D drawings and 3D modeling with high accuracy and precision. It’s compatible with common CAD files in DWG, DXF, DWT, PDF, JPG, and PNG. Also, it allows for customization with APIs like LISP, VBA, ZRX, and .NET to develop or migrate third-party applications. With ZWCAD, you can even directly transfer DWG or IFC format drawings with ARCHLine.XP, making CAD-BIM solutions easier.
Note:
ZWSOFT has released ZWCAD Flex, a subscription-based CAD solution currently available exclusively in the United States and Canada.
Users outside these regions are encouraged to contact their local ZWSOFT sales team to explore perpetual license options for ZWCAD.
As a lightweight CAD software, ZWCAD comes with an intuitive interface and useful features including File Compare which finds out the differences between two drawings simultaneously, Point Cloud which can process complex point clouds smoothly, Sheet Set Manager which enables you to view, access, manage, and plot multiple drawings in the same panel.
In addition, there are some incredible smart features exclusive to you, like Smart Mouse which can use mouse gestures to trigger commands easily, Smart Voice which lets you annotate the CAD file with your voice, etc. More importantly, ZWCAD requires a minimum specification of a computer with only 2GB RAM and 1GB graphics card, but works 1.7x faster than AutoCAD. Its perpetual license also makes it a great deal to enjoy forever updates and support after a one-time purchase.
Best BIM Software: Revit
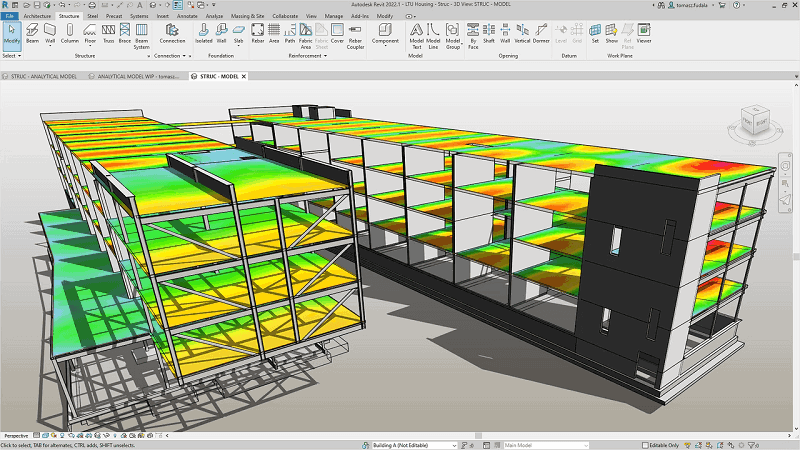
Revit is a well-known BIM software developed by Autodesk that offers an integrated platform for architects, engineers, designers, and construction professionals to create, analyze, and manage building information throughout the entire project lifecycle.
Unlike CAD software, Revit offers modeling toolsets for architecture, structure, MEP, and construction that enable you to create intelligent, parametric building models. It lets you quickly and precisely create dynamic, data-rich models with not only geometric information but also a wealth of essential data related to the building’s components, materials, specifications, and performance.
Also, it facilitates interdisciplinary collaboration and coordination with its centralized database. This ensures that multiple project team members can simultaneously work on various aspects of the project, exchange information, resolve conflicts, and coordinate changes in real-time. What’s more, it offers extensive tools to generate construction documentation. You can automatically generate plans, sections, elevations, schedules, and other essential drawings directly from the model.
FAQs About CAD and BIM
Will BIM Replace CAD?
This is not a simple question to answer. BIM and CAD each have unique characteristics and purposes. CAD is primarily used for drafting and design, especially in the realm of 2D drawings. On the other hand, BIM is more comprehensive and detailed which includes not only the 3D model of a building but also embeds rich architectural and engineering information. This makes BIM excel in aspects such as project lifecycle management, visualization, simulation, collaboration, and information sharing.
While BIM has significant advantages in many aspects, CAD still remains an important tool, especially for some simple drafting tasks. Additionally, many industry standards and workflows still rely on CAD. Therefore, BIM will not completely replace CAD but rather become a more powerful and comprehensive choice for specific projects and needs. In practical applications, many companies use CAD and BIM at the same time.
Should You Convert CAD to BIM?
The decision to convert CAD to BIM depends on the specific needs and goals of the project. Converting CAD to BIM is often most beneficial for complex projects, high collaboration capabilities, lifecycle maintenance, etc. BIM is a powerful tool that emphasizes data integration, collaboration, and long-term management. However, CAD may still be a more practical and cost-effective solution for small or less complex projects.
What Are the File Types of BIM and CAD?
Common BIM file formats are IFC, RVT, etc that contain building information for 3D modeling. They are usually used for BIM data exchange, collaboration, and analysis. Common CAD file formats include DWG, DXF, SAT, and TGES which store CAD drawings and models. They are used for exchanging CAD drawings between different programs.
BIM and CAD software often support other file formats for data exchange and interoperability. The choice of file format usually depends on the specific software used and the requirements of the project. In addition, some BIM software supports exporting DWG and DXF files for communication with CAD users.
Conclusion
After comparing BIM vs CAD, let’s jump to the conclusion. BIM and CAD have different applications and advantages in the fields of architecture, engineering, and construction. CAD is more suitable for simple design in 2D and 3D while BIM is for complicated building design in 3D with great collaboration. All in all, you may choose the appropriate tool based on the specific tasks and project requirements.
.png)